
Bioinformatics Workflows with evanverse
Source:vignettes/bioinformatics-workflows.Rmd
bioinformatics-workflows.Rmd🧬 Bioinformatics Workflows with evanverse
The evanverse package provides specialized tools for
common bioinformatics workflows, including gene ID conversion, gene set
analysis, pathway enrichment visualization, and biological data download
utilities. This comprehensive guide demonstrates practical applications
in genomics and systems biology.
🎯 Overview of Bioinformatics Functions
Core Bioinformatics Tools
| Function | Purpose | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
convert_gene_id() |
Gene identifier conversion | Symbol ↔︎ Ensembl, Entrez ↔︎ Symbol |
download_gene_ref() |
Reference genome downloads | Annotation files, gene models |
gmt2df() |
GMT file to data frame | Pathway analysis, gene set processing |
gmt2list() |
GMT file to named list | Enrichment analysis, functional annotation |
download_geo_data() |
GEO data retrieval | Public dataset analysis |
plot_venn() |
Venn diagram analysis | Gene set overlaps, differential expression |
🔄 Gene Identifier Conversion
Basic Gene ID Conversion
Gene identifier conversion is fundamental in bioinformatics for integrating datasets from different sources.
# Example gene symbols commonly used in cancer research
cancer_genes <- c("BRCA1", "BRCA2", "TP53", "EGFR", "MYC", "RAS", "PIK3CA", "AKT1")
# Convert gene symbols to Ensembl IDs
ensembl_ids <- convert_gene_id(
genes = cancer_genes,
from = "symbol",
to = "ensembl",
species = "human"
)
# Display conversion results
conversion_table <- data.frame(
Gene_Symbol = cancer_genes,
Ensembl_ID = ensembl_ids
)
print(conversion_table)
# Mock example for demonstration (since biomaRt requires internet)
cancer_genes <- c("BRCA1", "BRCA2", "TP53", "EGFR", "MYC", "KRAS", "PIK3CA", "AKT1")
# Simulated conversion results
mock_conversion <- data.frame(
Gene_Symbol = cancer_genes,
Ensembl_ID = c(
"ENSG00000012048", "ENSG00000139618", "ENSG00000141510",
"ENSG00000146648", "ENSG00000136997", "ENSG00000133703",
"ENSG00000171608", "ENSG00000142208"
),
Entrez_ID = c(672, 675, 7157, 1956, 4609, 3845, 5290, 207),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
cat("🧬 Gene ID Conversion Example\n")
#> 🧬 Gene ID Conversion Example
cat("=============================\n")
#> =============================
print(mock_conversion)
#> Gene_Symbol Ensembl_ID Entrez_ID
#> 1 BRCA1 ENSG00000012048 672
#> 2 BRCA2 ENSG00000139618 675
#> 3 TP53 ENSG00000141510 7157
#> 4 EGFR ENSG00000146648 1956
#> 5 MYC ENSG00000136997 4609
#> 6 KRAS ENSG00000133703 3845
#> 7 PIK3CA ENSG00000171608 5290
#> 8 AKT1 ENSG00000142208 207
cat("\n📊 Conversion Summary:\n")
#>
#> 📊 Conversion Summary:
cat(" • Input genes:", length(cancer_genes), "\n")
#> • Input genes: 8
cat(" • Successful conversions:", nrow(mock_conversion), "\n")
#> • Successful conversions: 8
cat(" • Success rate:", round(100 * nrow(mock_conversion) / length(cancer_genes), 1), "%\n")
#> • Success rate: 100 %Advanced Conversion Workflows
# Simulate a real-world scenario with mixed identifier types
mixed_identifiers <- c(
"BRCA1", "ENSG00000139618", "7157", "EGFR",
"ENSG00000136997", "3845", "PIK3CA", "207"
)
# Function to detect identifier type
detect_id_type <- function(ids) {
sapply(ids, function(id) {
if (grepl("^ENSG", id)) return("ensembl")
if (grepl("^[0-9]+$", id)) return("entrez")
return("symbol")
})
}
id_types <- detect_id_type(mixed_identifiers)
cat("🔍 Identifier Type Detection:\n")
#> 🔍 Identifier Type Detection:
print(data.frame(
Identifier = mixed_identifiers,
Detected_Type = id_types
))
#> Identifier Detected_Type
#> BRCA1 BRCA1 symbol
#> ENSG00000139618 ENSG00000139618 ensembl
#> 7157 7157 entrez
#> EGFR EGFR symbol
#> ENSG00000136997 ENSG00000136997 ensembl
#> 3845 3845 entrez
#> PIK3CA PIK3CA symbol
#> 207 207 entrez
# Group by identifier type for batch conversion
id_groups <- split(mixed_identifiers, id_types)
cat("\n📦 Grouped Identifiers for Conversion:\n")
#>
#> 📦 Grouped Identifiers for Conversion:
str(id_groups)
#> List of 3
#> $ ensembl: chr [1:2] "ENSG00000139618" "ENSG00000136997"
#> $ entrez : chr [1:3] "7157" "3845" "207"
#> $ symbol : chr [1:3] "BRCA1" "EGFR" "PIK3CA"📊 Gene Set Analysis with GMT Files
Processing GMT Files
GMT (Gene Matrix Transposed) files are standard formats for gene set collections used in pathway analysis.
# Example: Process a pathway GMT file
# pathway_df <- gmt2df("path/to/c2.cp.kegg.v7.4.symbols.gmt")
# pathway_list <- gmt2list("path/to/c2.cp.kegg.v7.4.symbols.gmt")
# Display structure
# head(pathway_df, 10)
# length(pathway_list)
# Create mock GMT data to demonstrate structure
mock_pathways <- list(
"KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS" = c(
"HK1", "HK2", "GPI", "PFKL", "ALDOA", "TPI1", "GAPDH",
"PGK1", "PGAM1", "ENO1", "PKM", "LDHA", "PDK1"
),
"KEGG_CITRATE_CYCLE" = c(
"CS", "ACO1", "IDH1", "OGDH", "SUCLA2", "SDHA",
"FH", "MDH1", "PCK1", "PDK1", "DLAT"
),
"KEGG_FATTY_ACID_SYNTHESIS" = c(
"ACACA", "FASN", "ACLY", "ACC2", "ELOVL6", "SCD",
"FADS1", "FADS2", "ACSL1", "GPAM"
),
"KEGG_DNA_REPAIR" = c(
"BRCA1", "BRCA2", "TP53", "ATM", "CHEK1", "CHEK2",
"RAD51", "XRCC1", "PARP1", "MSH2", "MLH1"
)
)
# Convert list to data frame format (simulating gmt2df output)
mock_gmt_df <- do.call(rbind, lapply(names(mock_pathways), function(pathway) {
data.frame(
pathway = pathway,
gene = mock_pathways[[pathway]],
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
}))
cat("📋 GMT File Processing Results\n")
#> 📋 GMT File Processing Results
cat("==============================\n")
#> ==============================
cat("Number of pathways:", length(mock_pathways), "\n")
#> Number of pathways: 4
cat("Total gene-pathway associations:", nrow(mock_gmt_df), "\n")
#> Total gene-pathway associations: 45
cat("Average genes per pathway:", round(mean(lengths(mock_pathways)), 1), "\n\n")
#> Average genes per pathway: 11.2
cat("Sample pathway data frame:\n")
#> Sample pathway data frame:
print(head(mock_gmt_df, 12))
#> pathway gene
#> 1 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS HK1
#> 2 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS HK2
#> 3 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS GPI
#> 4 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS PFKL
#> 5 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS ALDOA
#> 6 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS TPI1
#> 7 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS GAPDH
#> 8 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS PGK1
#> 9 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS PGAM1
#> 10 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS ENO1
#> 11 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS PKM
#> 12 KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS LDHA
# Pathway size distribution
pathway_sizes <- lengths(mock_pathways)
cat("\n📊 Pathway Size Distribution:\n")
#>
#> 📊 Pathway Size Distribution:
print(data.frame(
Pathway = names(pathway_sizes),
Gene_Count = pathway_sizes
))
#> Pathway Gene_Count
#> KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS KEGG_GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS 13
#> KEGG_CITRATE_CYCLE KEGG_CITRATE_CYCLE 11
#> KEGG_FATTY_ACID_SYNTHESIS KEGG_FATTY_ACID_SYNTHESIS 10
#> KEGG_DNA_REPAIR KEGG_DNA_REPAIR 11Gene Set Overlap Analysis
# Analyze overlaps between pathways
pathway_genes <- mock_pathways[1:3] # Use first 3 pathways for Venn diagram
# Create Venn diagram for pathway overlaps
venn_plot <- plot_venn(
set1 = pathway_genes[[1]],
set2 = pathway_genes[[2]],
set3 = pathway_genes[[3]],
category.names = names(pathway_genes),
fill = get_palette("qual_vivid", type = "qualitative", n = 3),
title = "Metabolic Pathway Gene Overlaps"
)
#> ✔ Loaded palette "qual_vivid" ("qualitative"), 9 colors
#> Warning: Using `size` aesthetic for lines was deprecated in ggplot2 3.4.0.
#> ℹ Please use `linewidth` instead.
#> ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the ggvenn package.
#> Please report the issue to the authors.
#> This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
#> Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
#> generated.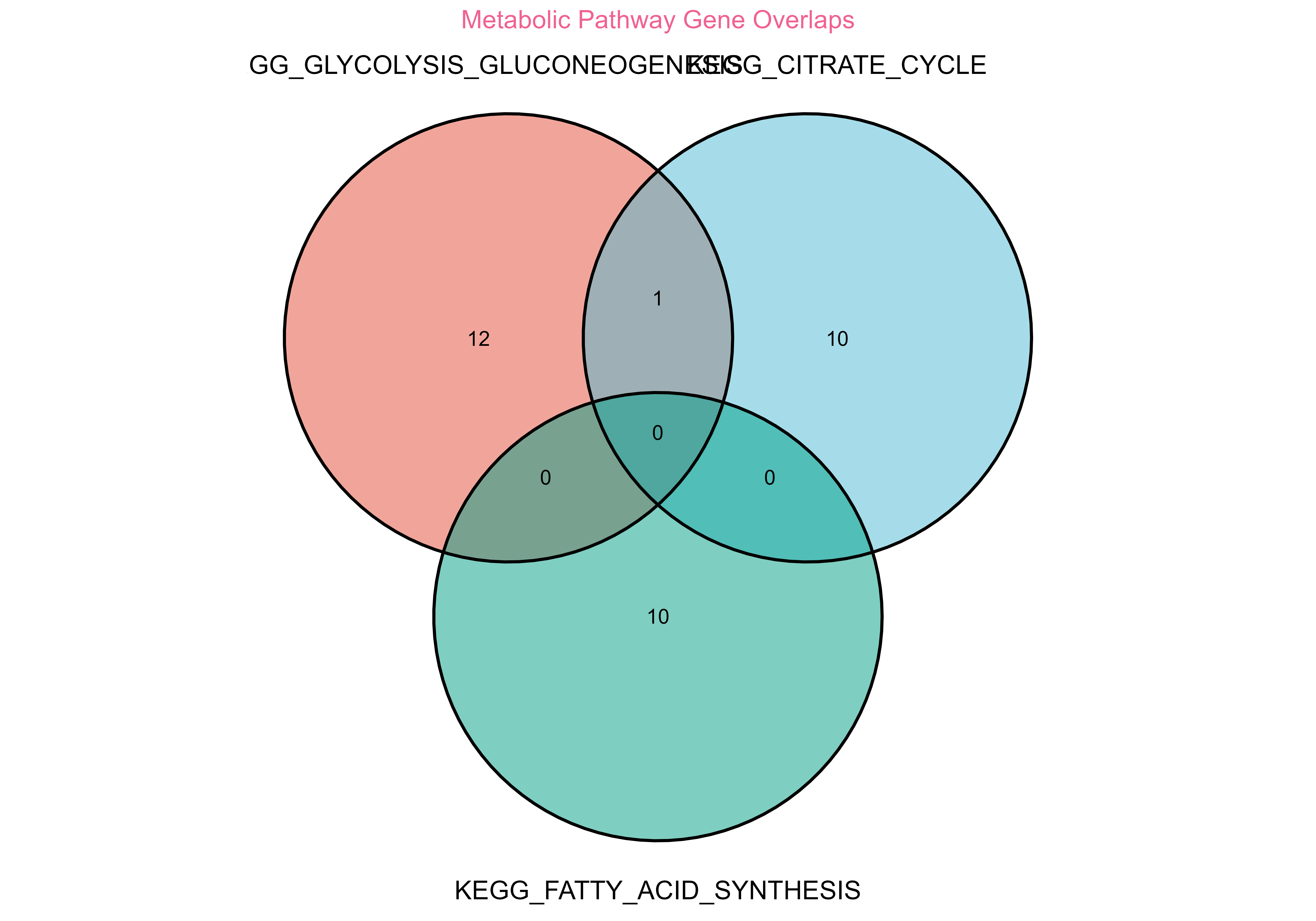
Gene set overlap analysis showing relationships between biological pathways
print(venn_plot)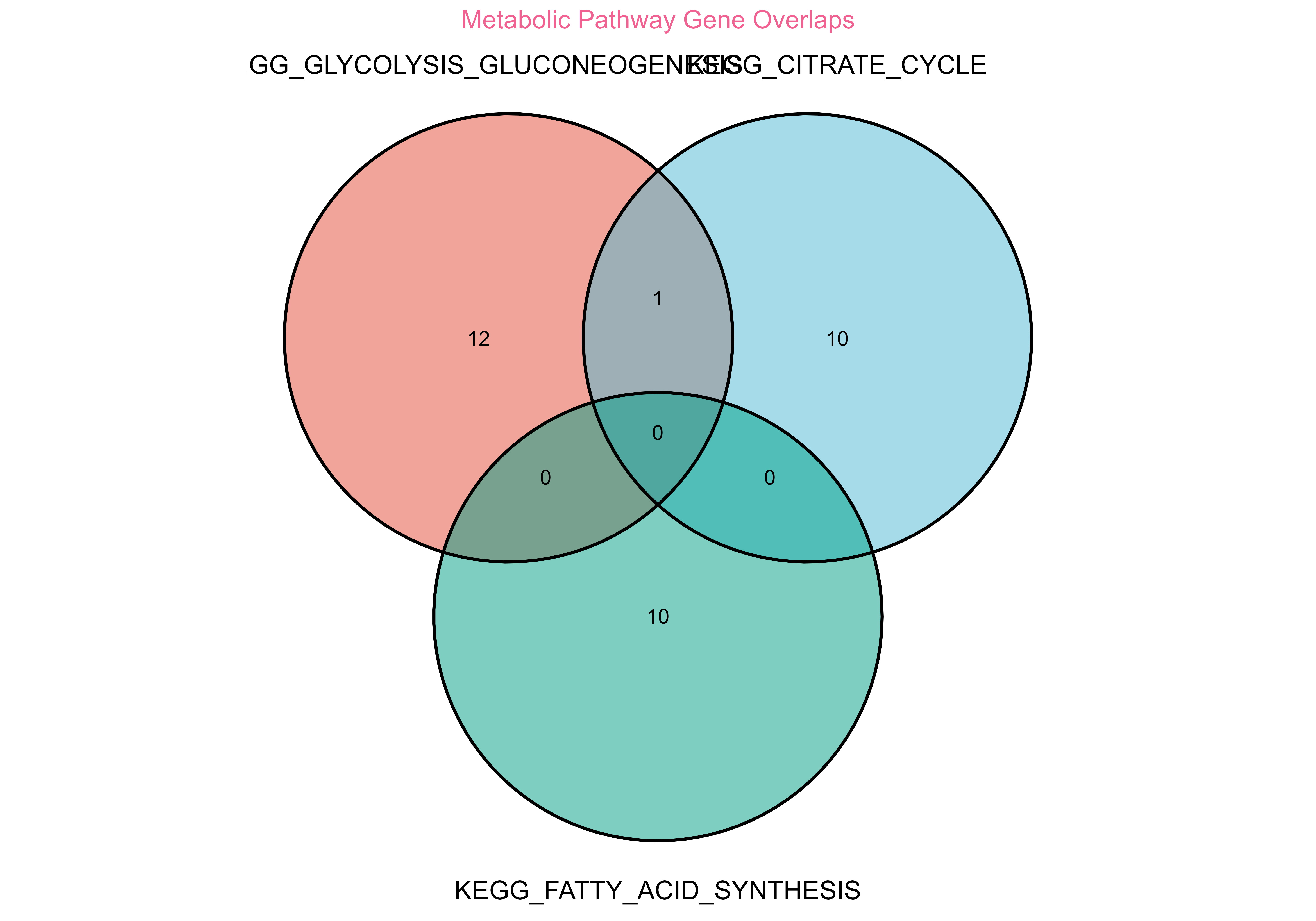
Gene set overlap analysis showing relationships between biological pathways
# Calculate detailed overlap statistics
all_genes <- unique(unlist(pathway_genes))
cat("\n🔍 Detailed Overlap Analysis:\n")
#>
#> 🔍 Detailed Overlap Analysis:
cat("===============================\n")
#> ===============================
cat("Total unique genes across pathways:", length(all_genes), "\n")
#> Total unique genes across pathways: 33
# Pairwise overlaps
pathway_names <- names(pathway_genes)
for (i in 1:(length(pathway_names) - 1)) {
for (j in (i + 1):length(pathway_names)) {
overlap <- length(intersect(pathway_genes[[i]], pathway_genes[[j]]))
cat(sprintf("%s ∩ %s: %d genes\n",
gsub("KEGG_", "", pathway_names[i]),
gsub("KEGG_", "", pathway_names[j]),
overlap))
}
}
#> GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS ∩ CITRATE_CYCLE: 1 genes
#> GLYCOLYSIS_GLUCONEOGENESIS ∩ FATTY_ACID_SYNTHESIS: 0 genes
#> CITRATE_CYCLE ∩ FATTY_ACID_SYNTHESIS: 0 genes🎯 Differential Expression Analysis Workflow
Simulated RNA-seq Analysis
# Simulate RNA-seq differential expression results
set.seed(123)
n_genes <- 2000
# Simulate log fold changes and p-values
gene_results <- data.frame(
Gene = paste0("Gene_", 1:n_genes),
LogFC = rnorm(n_genes, mean = 0, sd = 1.2),
PValue = rbeta(n_genes, shape1 = 1, shape2 = 10),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
# Add some significant genes
significant_indices <- sample(1:n_genes, 200)
gene_results$LogFC[significant_indices] <- gene_results$LogFC[significant_indices] +
sample(c(-2, 2), 200, replace = TRUE)
gene_results$PValue[significant_indices] <- gene_results$PValue[significant_indices] * 0.01
# Calculate adjusted p-values
gene_results$FDR <- p.adjust(gene_results$PValue, method = "BH")
# Classify genes
gene_results$Regulation <- "Not Significant"
gene_results$Regulation[gene_results$FDR < 0.05 & gene_results$LogFC > 1] <- "Up-regulated"
gene_results$Regulation[gene_results$FDR < 0.05 & gene_results$LogFC < -1] <- "Down-regulated"
# Create volcano plot
volcano_colors <- c(
"Up-regulated" = get_palette("qual_vivid", type = "qualitative", n = 3)[1],
"Down-regulated" = get_palette("qual_vivid", type = "qualitative", n = 3)[2],
"Not Significant" = "#CCCCCC"
)
#> ✔ Loaded palette "qual_vivid" ("qualitative"), 9 colors
#> ✔ Loaded palette "qual_vivid" ("qualitative"), 9 colors
p1 <- ggplot(gene_results, aes(x = LogFC, y = -log10(FDR), color = Regulation)) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.6, size = 1.2) +
scale_color_manual(values = volcano_colors) +
geom_vline(xintercept = c(-1, 1), linetype = "dashed", color = "#666666") +
geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(0.05), linetype = "dashed", color = "#666666") +
labs(
title = "Differential Gene Expression Analysis",
subtitle = "Volcano plot showing treatment vs. control comparison",
x = "Log₂ Fold Change",
y = "-log₁₀(FDR-adjusted p-value)",
color = "Regulation"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(size = 14, face = "bold", color = "#0D47A1"),
plot.subtitle = element_text(size = 11, color = "#666666"),
legend.position = "bottom"
)
print(p1)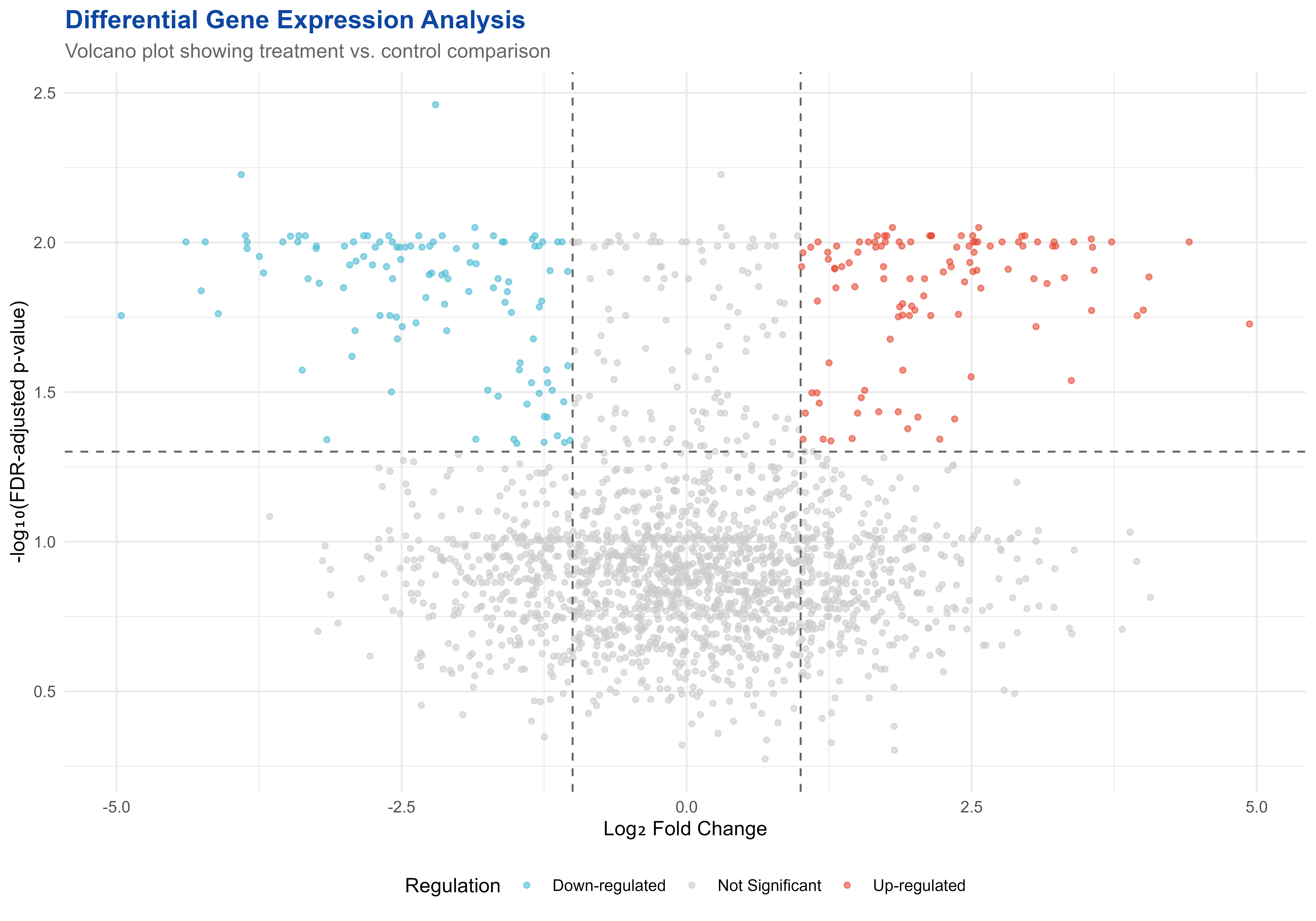
Differential expression analysis visualization with volcano plot
# Summary statistics
regulation_summary <- table(gene_results$Regulation)
cat("\n📊 Differential Expression Summary:\n")
#>
#> 📊 Differential Expression Summary:
cat("===================================\n")
#> ===================================
print(regulation_summary)
#>
#> Down-regulated Not Significant Up-regulated
#> 113 1777 110
cat("\nTop 10 up-regulated genes (by fold change):\n")
#>
#> Top 10 up-regulated genes (by fold change):
top_up <- gene_results[gene_results$Regulation == "Up-regulated", ] %>%
arrange(desc(LogFC)) %>%
head(10)
print(top_up[, c("Gene", "LogFC", "FDR")])
#> Gene LogFC FDR
#> 1 Gene_1911 4.937598 0.018718628
#> 2 Gene_948 4.408017 0.009956437
#> 3 Gene_477 4.054766 0.013037421
#> 4 Gene_343 4.005266 0.016821175
#> 5 Gene_489 3.952257 0.017546948
#> 6 Gene_1189 3.727714 0.009956437
#> 7 Gene_202 3.574896 0.012378355
#> 8 Gene_264 3.560238 0.010369230
#> 9 Gene_1926 3.551683 0.016873989
#> 10 Gene_1255 3.549588 0.009735872Pathway Enrichment Analysis
# Simulate pathway enrichment analysis results
enrichment_results <- data.frame(
Pathway = c(
"Cell Cycle", "Apoptosis", "DNA Repair", "Inflammation",
"Metabolism", "Signaling", "Transport", "Development"
),
GeneRatio = c(0.15, 0.22, 0.18, 0.31, 0.09, 0.25, 0.12, 0.08),
FDR = c(0.001, 0.003, 0.008, 0.0001, 0.045, 0.002, 0.021, 0.089),
GeneCount = c(23, 34, 28, 48, 14, 39, 18, 12),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
# Calculate enrichment score
enrichment_results$EnrichmentScore <- -log10(enrichment_results$FDR)
# Create enrichment plot
p2 <- ggplot(enrichment_results, aes(x = GeneRatio, y = reorder(Pathway, EnrichmentScore))) +
geom_point(aes(color = EnrichmentScore, size = GeneCount), alpha = 0.8) +
scale_color_gradientn(
colors = get_palette("seq_blush", type = "sequential", n = 4),
name = "-log₁₀(FDR)"
) +
scale_size_continuous(name = "Gene Count", range = c(3, 12)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0.1, linetype = "dashed", color = "#666666", alpha = 0.7) +
labs(
title = "Pathway Enrichment Analysis",
subtitle = "Biological processes enriched in differentially expressed genes",
x = "Gene Ratio (enriched genes / pathway total)",
y = "Biological Pathway"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(size = 14, face = "bold", color = "#0D47A1"),
plot.subtitle = element_text(size = 11, color = "#666666"),
panel.grid.major.y = element_blank(),
legend.position = "right"
)
#> ✔ Loaded palette "seq_blush" ("sequential"), 4 colors
print(p2)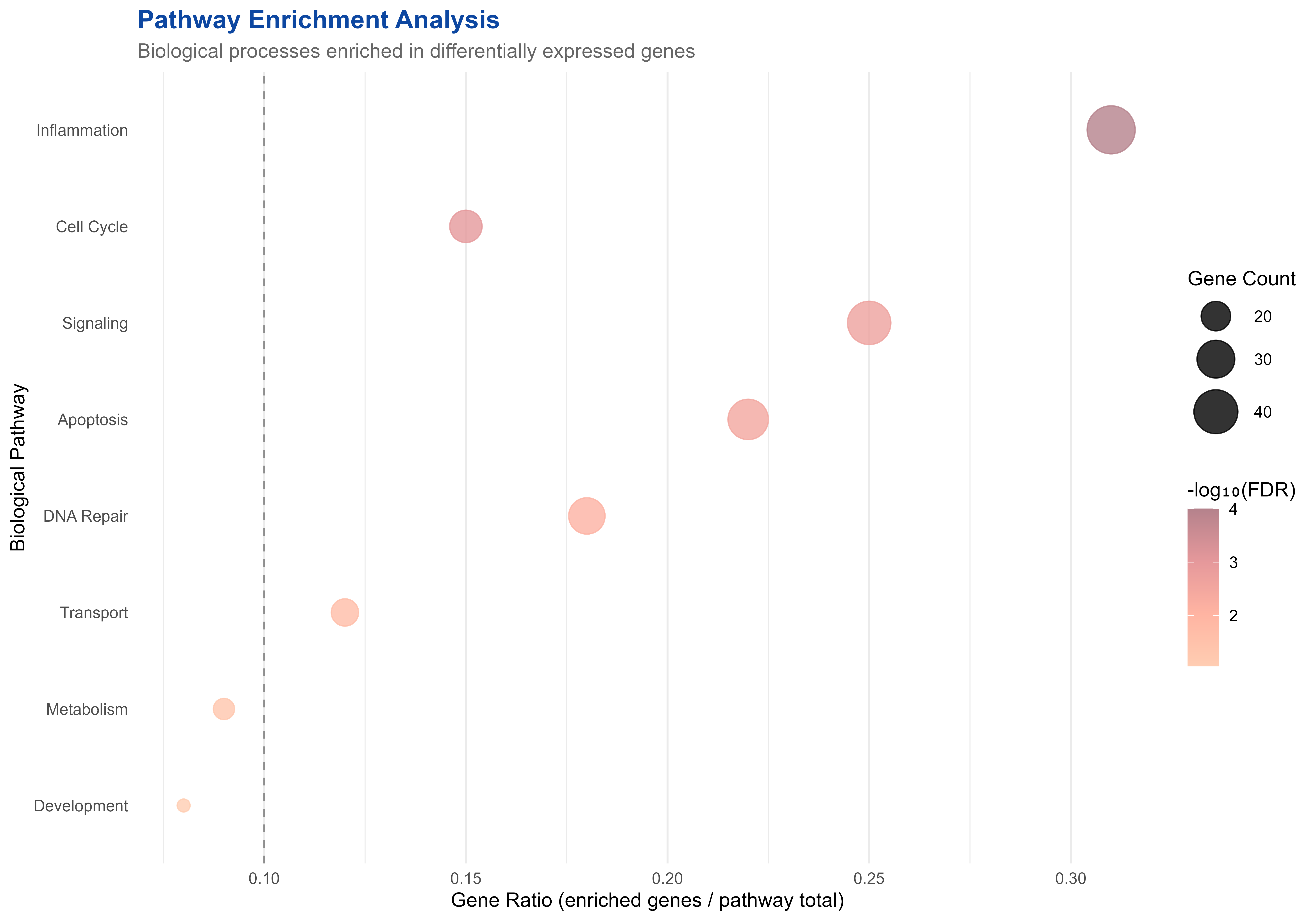
Pathway enrichment analysis showing biological processes affected by treatment
cat("\n🎯 Pathway Enrichment Summary:\n")
#>
#> 🎯 Pathway Enrichment Summary:
cat("==============================\n")
#> ==============================
significant_pathways <- enrichment_results[enrichment_results$FDR < 0.05, ]
cat("Significant pathways (FDR < 0.05):", nrow(significant_pathways), "\n")
#> Significant pathways (FDR < 0.05): 7
cat("Most enriched pathway:", significant_pathways$Pathway[which.max(significant_pathways$EnrichmentScore)], "\n")
#> Most enriched pathway: Inflammation
cat("Total genes in significant pathways:", sum(significant_pathways$GeneCount), "\n")
#> Total genes in significant pathways: 204🌐 Multi-omics Integration
Combining Genomics and Transcriptomics
# Simulate multi-omics data integration
set.seed(456)
selected_genes <- c("BRCA1", "TP53", "EGFR", "MYC", "KRAS", "PIK3CA", "AKT1", "PTEN")
# Create integrated omics data
omics_data <- data.frame(
Gene = rep(selected_genes, each = 3),
DataType = rep(c("Mutation", "CNV", "Expression"), length(selected_genes)),
Value = c(
# Mutation frequencies (0-1)
c(0.12, 0.34, 0.08, 0.15, 0.22, 0.09, 0.06, 0.18),
# Copy number variations (-2 to 2)
c(-0.5, -1.2, 1.8, 0.3, 0.8, -0.8, 1.1, -1.5),
# Expression fold changes (-3 to 3)
c(-1.5, -2.8, 2.1, 1.8, -1.2, 2.3, -0.8, -2.1)
),
Patient_Group = rep(c("Group_A", "Group_B", "Group_C"), length(selected_genes))
)
# Normalize values for visualization
omics_data$Normalized_Value <- ave(omics_data$Value, omics_data$DataType,
FUN = function(x) scale(x)[,1])
# Create heatmap
p3 <- ggplot(omics_data, aes(x = DataType, y = Gene, fill = Normalized_Value)) +
geom_tile(color = "white", size = 0.5) +
scale_fill_gradientn(
colors = get_palette("div_contrast", type = "diverging"),
name = "Z-score",
limits = c(-2, 2),
breaks = c(-2, -1, 0, 1, 2)
) +
labs(
title = "Multi-omics Cancer Gene Analysis",
subtitle = "Integrated view of mutations, copy number, and expression",
x = "Data Type",
y = "Cancer-related Genes"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(size = 14, face = "bold", color = "#0D47A1"),
plot.subtitle = element_text(size = 11, color = "#666666"),
panel.grid = element_blank(),
axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1)
)
#> ✔ Loaded palette "div_contrast" ("diverging"), 2 colors
print(p3)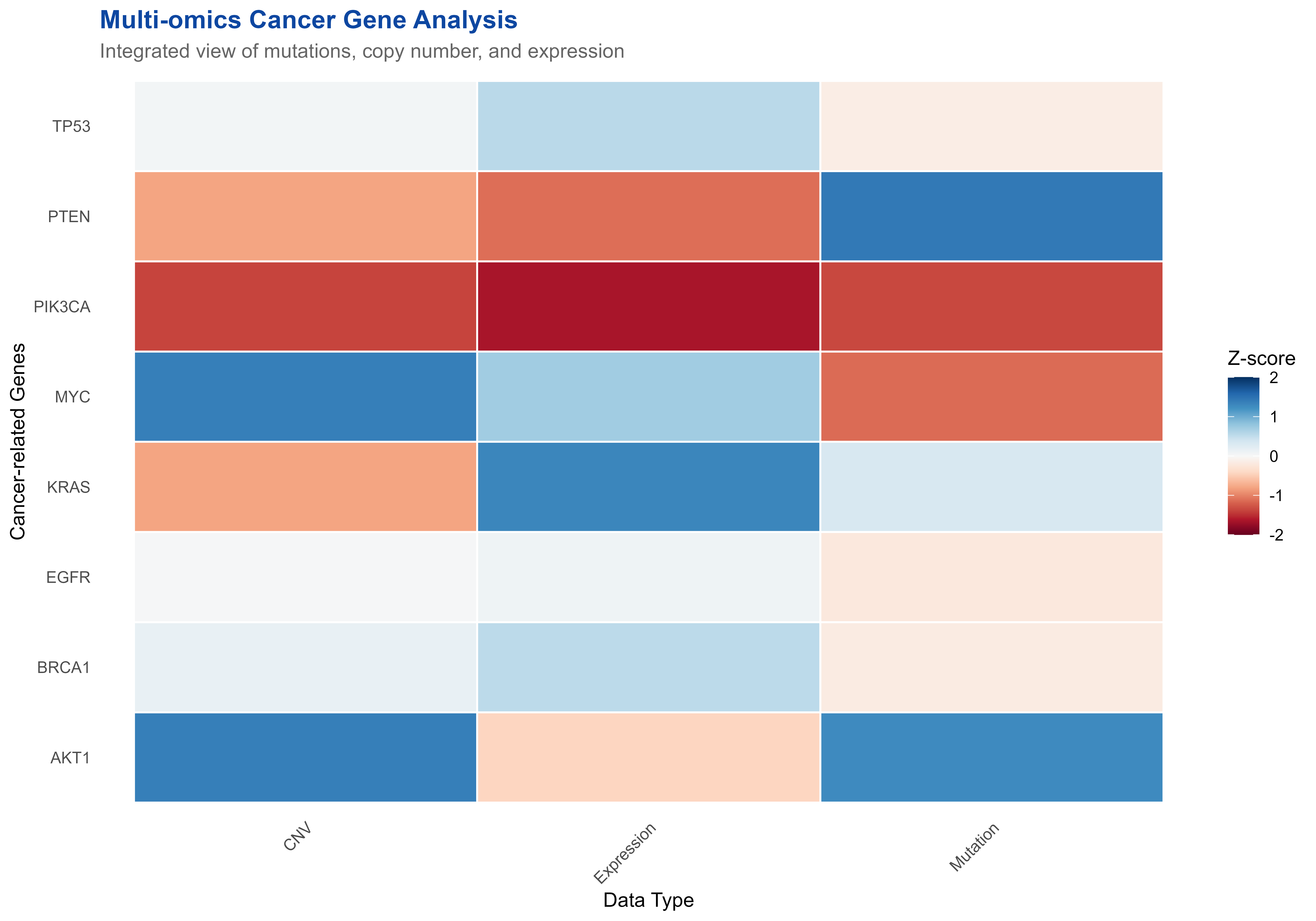
Multi-omics data integration showing genomic variants and expression changes
# Summary by data type
cat("\n🧬 Multi-omics Data Summary:\n")
#>
#> 🧬 Multi-omics Data Summary:
cat("============================\n")
#> ============================
summary_stats <- omics_data %>%
group_by(DataType) %>%
summarise(
Mean_Value = round(mean(Value), 3),
SD_Value = round(sd(Value), 3),
Min_Value = round(min(Value), 3),
Max_Value = round(max(Value), 3),
.groups = 'drop'
)
print(summary_stats)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 5
#> DataType Mean_Value SD_Value Min_Value Max_Value
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 CNV 0.155 1.20 -1.5 1.8
#> 2 Expression -0.629 1.31 -2.8 1.1
#> 3 Mutation 0.354 1.37 -1.5 2.3🔬 Clinical Data Integration
Biomarker Discovery Pipeline
# Simulate clinical biomarker data
set.seed(789)
n_patients <- 120
n_biomarkers <- 20
# Generate patient clinical data
clinical_data <- data.frame(
Patient_ID = paste0("P", 1:n_patients),
Subtype = sample(c("Luminal_A", "Luminal_B", "HER2+", "TNBC"), n_patients,
replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.4, 0.2, 0.15, 0.25)),
Stage = sample(c("I", "II", "III", "IV"), n_patients,
replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.3, 0.35, 0.25, 0.1)),
Age = round(rnorm(n_patients, 55, 12)),
Survival_Months = round(rexp(n_patients, rate = 0.02)),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
# Generate biomarker expression data
biomarker_genes <- paste0("Biomarker_", 1:n_biomarkers)
expression_data <- matrix(rnorm(n_patients * n_biomarkers, mean = 5, sd = 2),
nrow = n_patients, ncol = n_biomarkers)
colnames(expression_data) <- biomarker_genes
rownames(expression_data) <- clinical_data$Patient_ID
# Add subtype-specific expression patterns
luminal_a_patients <- clinical_data$Patient_ID[clinical_data$Subtype == "Luminal_A"]
her2_patients <- clinical_data$Patient_ID[clinical_data$Subtype == "HER2+"]
tnbc_patients <- clinical_data$Patient_ID[clinical_data$Subtype == "TNBC"]
# Simulate subtype-specific biomarkers
expression_data[luminal_a_patients, "Biomarker_1"] <-
expression_data[luminal_a_patients, "Biomarker_1"] + 3
expression_data[her2_patients, "Biomarker_5"] <-
expression_data[her2_patients, "Biomarker_5"] + 4
expression_data[tnbc_patients, "Biomarker_12"] <-
expression_data[tnbc_patients, "Biomarker_12"] + 2.5
# Convert to long format for visualization
expression_long <- as.data.frame(expression_data) %>%
mutate(Patient_ID = rownames(.)) %>%
gather(Biomarker, Expression, -Patient_ID) %>%
left_join(clinical_data, by = "Patient_ID")
# Select top biomarkers for visualization
top_biomarkers <- c("Biomarker_1", "Biomarker_5", "Biomarker_12", "Biomarker_8")
plot_data <- expression_long %>%
filter(Biomarker %in% top_biomarkers)
# Create biomarker expression plot
p5 <- ggplot(plot_data, aes(x = Subtype, y = Expression, fill = Subtype)) +
geom_boxplot(alpha = 0.7, outlier.alpha = 0.5) +
geom_jitter(alpha = 0.3, width = 0.2, size = 0.8) +
scale_fill_manual(
values = get_palette("qual_vivid", type = "qualitative", n = 4)
) +
facet_wrap(~Biomarker, scales = "free_y", ncol = 2) +
labs(
title = "Biomarker Expression Across Cancer Subtypes",
subtitle = "Potential subtype-specific biomarkers for precision medicine",
x = "Cancer Subtype",
y = "Expression Level (log2 normalized)",
fill = "Subtype"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
plot.title = element_text(size = 14, face = "bold", color = "#0D47A1"),
plot.subtitle = element_text(size = 11, color = "#666666"),
axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1),
legend.position = "bottom",
strip.background = element_rect(fill = "#E3F2FD", color = NA)
)
#> ✔ Loaded palette "qual_vivid" ("qualitative"), 9 colors
print(p5)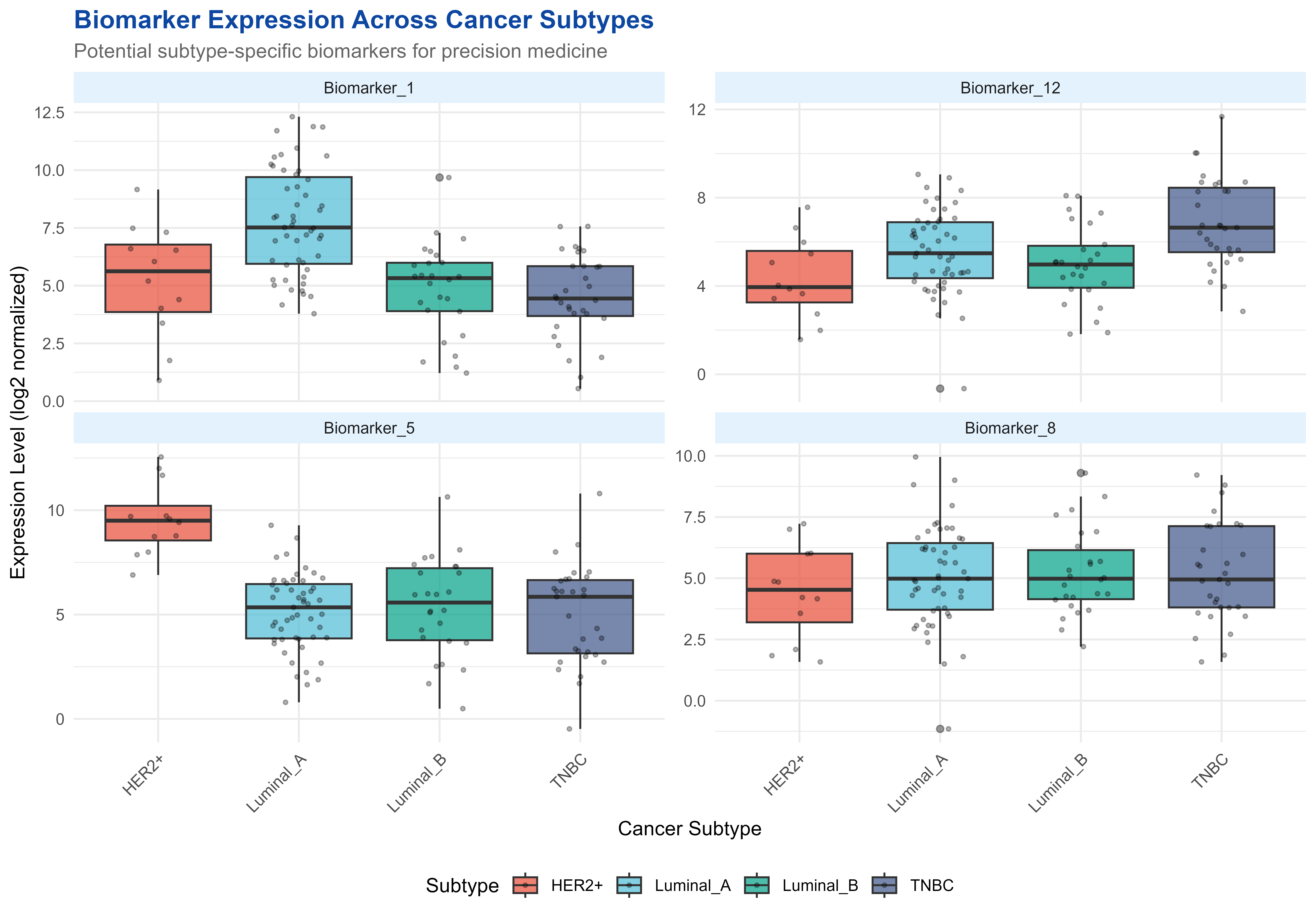
Biomarker discovery showing gene expression patterns across clinical subtypes
# Statistical summary
cat("\n📊 Biomarker Analysis Summary:\n")
#>
#> 📊 Biomarker Analysis Summary:
cat("==============================\n")
#> ==============================
subtype_counts <- table(clinical_data$Subtype)
print(subtype_counts)
#>
#> HER2+ Luminal_A Luminal_B TNBC
#> 12 51 26 31
cat("\nMean expression by subtype for key biomarkers:\n")
#>
#> Mean expression by subtype for key biomarkers:
biomarker_summary <- plot_data %>%
group_by(Biomarker, Subtype) %>%
summarise(
Mean_Expression = round(mean(Expression), 2),
SD = round(sd(Expression), 2),
.groups = 'drop'
) %>%
arrange(Biomarker, desc(Mean_Expression))
print(biomarker_summary)
#> # A tibble: 16 × 4
#> Biomarker Subtype Mean_Expression SD
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Biomarker_1 Luminal_A 7.76 2.29
#> 2 Biomarker_1 HER2+ 5.23 2.44
#> 3 Biomarker_1 Luminal_B 4.84 2.02
#> 4 Biomarker_1 TNBC 4.54 1.84
#> 5 Biomarker_12 TNBC 6.88 2.01
#> 6 Biomarker_12 Luminal_A 5.55 1.87
#> 7 Biomarker_12 Luminal_B 4.97 1.77
#> 8 Biomarker_12 HER2+ 4.33 1.85
#> 9 Biomarker_5 HER2+ 9.58 1.74
#> 10 Biomarker_5 Luminal_B 5.36 2.34
#> 11 Biomarker_5 Luminal_A 5.11 1.85
#> 12 Biomarker_5 TNBC 4.98 2.37
#> 13 Biomarker_8 Luminal_B 5.23 1.74
#> 14 Biomarker_8 TNBC 5.22 2.03
#> 15 Biomarker_8 Luminal_A 5.08 2.05
#> 16 Biomarker_8 HER2+ 4.45 1.93🛠️ Data Download and Management
Public Dataset Retrieval
# Example of downloading reference data
# Note: These functions require internet connection and may take time
# Download gene reference annotation
gene_ref <- download_gene_ref(
species = "human",
build = "hg38",
feature_type = "gene"
)
# Download GEO dataset
geo_data <- download_geo_data(
geo_id = "GSE123456",
destdir = "data/geo_downloads"
)
# Download pathway databases
pathway_url <- "https://data.broadinstitute.org/gsea-msigdb/msigdb/release/7.4/c2.cp.kegg.v7.4.symbols.gmt"
download_url(
url = pathway_url,
dest = "data/pathways/kegg_pathways.gmt"
)
# Demonstrate file organization for bioinformatics projects
cat("📁 Recommended Project Structure for Bioinformatics:\n")
#> 📁 Recommended Project Structure for Bioinformatics:
cat("==================================================\n")
#> ==================================================
cat("project/\n")
#> project/
cat("├── data/\n")
#> ├── data/
cat("│ ├── raw/ # Original data files\n")
#> │ ├── raw/ # Original data files
cat("│ ├── processed/ # Cleaned/normalized data\n")
#> │ ├── processed/ # Cleaned/normalized data
cat("│ ├── reference/ # Genome annotations, databases\n")
#> │ ├── reference/ # Genome annotations, databases
cat("│ └── results/ # Analysis outputs\n")
#> │ └── results/ # Analysis outputs
cat("├── scripts/\n")
#> ├── scripts/
cat("│ ├── preprocessing/ # Data cleaning scripts\n")
#> │ ├── preprocessing/ # Data cleaning scripts
cat("│ ├── analysis/ # Statistical analysis\n")
#> │ ├── analysis/ # Statistical analysis
cat("│ └── visualization/ # Plotting scripts\n")
#> │ └── visualization/ # Plotting scripts
cat("├── docs/ # Documentation, protocols\n")
#> ├── docs/ # Documentation, protocols
cat("└── reports/ # Final reports, publications\n\n")
#> └── reports/ # Final reports, publications
# Demonstrate batch file handling
file_extensions <- c("fastq.gz", "bam", "vcf", "gmt", "gff3", "bed")
file_descriptions <- c(
"Raw sequencing reads",
"Aligned sequencing data",
"Variant calls",
"Gene set definitions",
"Gene annotations",
"Genomic intervals"
)
file_info <- data.frame(
Extension = file_extensions,
Description = file_descriptions,
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
cat("🗂️ Common Bioinformatics File Types:\n")
#> 🗂️ Common Bioinformatics File Types:
print(file_info)
#> Extension Description
#> 1 fastq.gz Raw sequencing reads
#> 2 bam Aligned sequencing data
#> 3 vcf Variant calls
#> 4 gmt Gene set definitions
#> 5 gff3 Gene annotations
#> 6 bed Genomic intervals🎯 Best Practices for Bioinformatics Workflows
Reproducible Analysis Guidelines
cat("🔬 BIOINFORMATICS BEST PRACTICES\n")
#> 🔬 BIOINFORMATICS BEST PRACTICES
cat("================================\n\n")
#> ================================
cat("📋 Data Management:\n")
#> 📋 Data Management:
cat(" • Use version control (Git) for all scripts\n")
#> • Use version control (Git) for all scripts
cat(" • Document data provenance and processing steps\n")
#> • Document data provenance and processing steps
cat(" • Implement checkpoints and intermediate file saves\n")
#> • Implement checkpoints and intermediate file saves
cat(" • Use consistent file naming conventions\n\n")
#> • Use consistent file naming conventions
cat("🧬 Gene Identifier Handling:\n")
#> 🧬 Gene Identifier Handling:
cat(" • Always validate gene ID conversions\n")
#> • Always validate gene ID conversions
cat(" • Store original identifiers alongside converted ones\n")
#> • Store original identifiers alongside converted ones
cat(" • Document the genome build and annotation version\n")
#> • Document the genome build and annotation version
cat(" • Handle missing/ambiguous identifiers gracefully\n\n")
#> • Handle missing/ambiguous identifiers gracefully
cat("📊 Statistical Analysis:\n")
#> 📊 Statistical Analysis:
cat(" • Apply appropriate multiple testing corrections\n")
#> • Apply appropriate multiple testing corrections
cat(" • Set significance thresholds before analysis\n")
#> • Set significance thresholds before analysis
cat(" • Report effect sizes along with p-values\n")
#> • Report effect sizes along with p-values
cat(" • Validate results with independent datasets when possible\n\n")
#> • Validate results with independent datasets when possible
cat("🎨 Visualization Guidelines:\n")
#> 🎨 Visualization Guidelines:
cat(" • Use color-blind friendly palettes\n")
#> • Use color-blind friendly palettes
cat(" • Include appropriate scales and legends\n")
#> • Include appropriate scales and legends
cat(" • Provide clear titles and axis labels\n")
#> • Provide clear titles and axis labels
cat(" • Consider publication requirements for figures\n")
#> • Consider publication requirements for figuresQuality Control Checklist
cat("✅ QUALITY CONTROL CHECKLIST\n")
#> ✅ QUALITY CONTROL CHECKLIST
cat("============================\n\n")
#> ============================
cat("🔍 Data Quality:\n")
#> 🔍 Data Quality:
cat(" [ ] Check for missing values and outliers\n")
#> [ ] Check for missing values and outliers
cat(" [ ] Verify sample sizes and statistical power\n")
#> [ ] Verify sample sizes and statistical power
cat(" [ ] Validate gene identifier mappings\n")
#> [ ] Validate gene identifier mappings
cat(" [ ] Assess data distribution and normalization\n\n")
#> [ ] Assess data distribution and normalization
cat("📈 Analysis Validation:\n")
#> 📈 Analysis Validation:
cat(" [ ] Cross-validate results with different methods\n")
#> [ ] Cross-validate results with different methods
cat(" [ ] Perform sensitivity analyses\n")
#> [ ] Perform sensitivity analyses
cat(" [ ] Check for batch effects and confounders\n")
#> [ ] Check for batch effects and confounders
cat(" [ ] Compare with known biological expectations\n\n")
#> [ ] Compare with known biological expectations
cat("📊 Results Reporting:\n")
#> 📊 Results Reporting:
cat(" [ ] Include sample sizes and effect sizes\n")
#> [ ] Include sample sizes and effect sizes
cat(" [ ] Report confidence intervals\n")
#> [ ] Report confidence intervals
cat(" [ ] Document software versions and parameters\n")
#> [ ] Document software versions and parameters
cat(" [ ] Provide supplementary data and code\n")
#> [ ] Provide supplementary data and code🚀 Advanced Workflow Examples
Complete Analysis Pipeline
cat("🔄 COMPLETE BIOINFORMATICS PIPELINE EXAMPLE\n")
#> 🔄 COMPLETE BIOINFORMATICS PIPELINE EXAMPLE
cat("===========================================\n\n")
#> ===========================================
# Simulate a complete analysis workflow
pipeline_steps <- data.frame(
Step = 1:8,
Process = c(
"Data Import & Quality Control",
"Gene ID Conversion & Mapping",
"Differential Expression Analysis",
"Multiple Testing Correction",
"Pathway Enrichment Analysis",
"Gene Set Overlap Analysis",
"Visualization & Plotting",
"Results Export & Reporting"
),
evanverse_Functions = c(
"read_table_flex(), file_info()",
"convert_gene_id(), replace_void()",
"User analysis + evanverse utilities",
"Built-in R functions",
"gmt2df(), gmt2list()",
"plot_venn(), combine_logic()",
"get_palette(), plot_*() functions",
"write_xlsx_flex(), remind()"
),
Estimated_Time = c("5-10 min", "10-15 min", "30-60 min", "5 min",
"15-30 min", "10-20 min", "20-40 min", "10-15 min")
)
print(pipeline_steps)
#> Step Process evanverse_Functions
#> 1 1 Data Import & Quality Control read_table_flex(), file_info()
#> 2 2 Gene ID Conversion & Mapping convert_gene_id(), replace_void()
#> 3 3 Differential Expression Analysis User analysis + evanverse utilities
#> 4 4 Multiple Testing Correction Built-in R functions
#> 5 5 Pathway Enrichment Analysis gmt2df(), gmt2list()
#> 6 6 Gene Set Overlap Analysis plot_venn(), combine_logic()
#> 7 7 Visualization & Plotting get_palette(), plot_*() functions
#> 8 8 Results Export & Reporting write_xlsx_flex(), remind()
#> Estimated_Time
#> 1 5-10 min
#> 2 10-15 min
#> 3 30-60 min
#> 4 5 min
#> 5 15-30 min
#> 6 10-20 min
#> 7 20-40 min
#> 8 10-15 min
cat("\n⏱️ Total Estimated Pipeline Time: 2-4 hours\n")
#>
#> ⏱️ Total Estimated Pipeline Time: 2-4 hours
cat("🎯 Key Success Factors:\n")
#> 🎯 Key Success Factors:
cat(" • Proper data validation at each step\n")
#> • Proper data validation at each step
cat(" • Consistent identifier handling\n")
#> • Consistent identifier handling
cat(" • Appropriate statistical methods\n")
#> • Appropriate statistical methods
cat(" • Clear documentation and visualization\n")
#> • Clear documentation and visualization🎯 Summary and Next Steps
The evanverse bioinformatics toolkit provides:
✅ Gene identifier conversion with species and build support ✅ Pathway analysis tools for GMT file processing ✅ Visualization functions optimized for biological data ✅ Data download utilities for public repositories ✅ Multi-omics integration capabilities ✅ Quality control helpers for robust analysis
Continue Learning:
- 📊 Package Management - Advanced installation techniques
- 🎨 Color Palette Guide - Bioinformatics color schemes
- 📚 Comprehensive Guide - Complete package overview
Essential Bioinformatics Functions:
# Gene identifier conversion
convert_gene_id(genes, from = "symbol", to = "ensembl", species = "human")
# Pathway analysis
pathways <- gmt2list("pathways.gmt")
plot_venn(gene_sets, colors = get_palette("qual_vivid"))
# Data visualization
get_palette("div_contrast", type = "diverging")
plot_venn(gene_sets)
# Data management
download_geo_data("GSE123456")
read_table_flex("expression_data.txt")🧬 Accelerate your bioinformatics research with evanverse!